Zero Crossing Detector
Aim
To design and simulate a Zero Crossing Detector circuit.
Components
|
Name
|
EDWin Components Used |
Description |
Number of components
required |
| TRANSFORMER |
SMB_TRANSFORMER |
Transformer |
1 |
| RES |
RC05 |
Resistor |
3 |
| DIODE |
1N4007 |
Diode |
5 |
| VGEN |
VGEN |
Ac voltage source |
1 |
| GND |
SPL0 |
Ground |
1 |
| NPN |
BC107 |
Transistor |
1 |
| CAP |
CAP |
Capacitor |
1 |
Theory
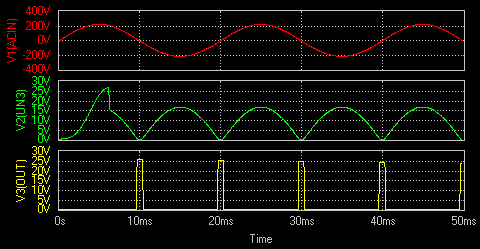
As the name indicates the zero crossing detector
is a device for detecting the point where the voltage crosses zero in either direction.
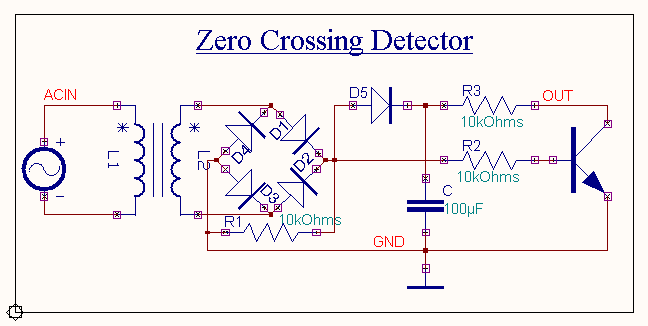
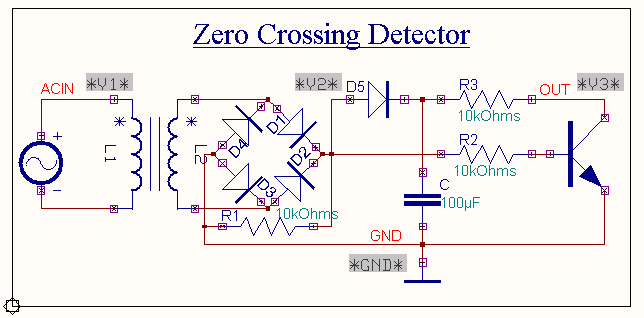
As shown in the above circuit diagram the first section is a
bridge rectifier, which provides full wave rectified output. This is
applied to the base of the transistor through a base resistor, R2. The
capacitor charges to maximum of the bridge rectified output through the diode,D5. This
charge is available to the transistor as VCC. The capacitance value is kept large in order to
minimize ripple and get perfect dc. The transistor remains OFF until the
Cut-in voltage VBE is
reached. During the OFF period of the transistor the output will be high and approximately
equal to VCC. Once the
transistor is ON and IB increases according to the input wave,
the transistor moves slowly towards saturation where the output reduces to
the saturation voltage of the transistor which is nearly equal to
zero.
Initially VBE = Cut-in voltage of diode, the
capacitor will charge through the diode Vm where Vm
is
the maximum amplitude of the rectified wave. Now
the diode is reverse biased and hence does not provide a discharging path for the
capacitor, which in turn has two effects.
Vm where Vm
is
the maximum amplitude of the rectified wave. Now
the diode is reverse biased and hence does not provide a discharging path for the
capacitor, which in turn has two effects.
- Variation in VCC.
- It will provide base current to the transistor in the region where both diode and
transistor are OFF.
Thus an output square wave is produced whenever the input voltage
crosses zero thereby acting as a zero crossing detector.
Procedure
EDWinXP -> Schematic Editor: The circuit diagram is drawn by
loading components from the library.
Wiring and proper
net assignment has been made. The values are assigned for relevant
components.
EDWinXP -> Mixed Mode Simulator: The circuit is preprocessed. The waveform markers are
placed at transformer primary, bridge output and detector output. The Transient Analysis parameters have been set. The Transient Analysis is
executed and output observed in the Waveform Viewer.
Result
The output waveform may be observed in the waveform viewer.