Series and Parallel Resistances
Aim
To find out the effective of the multiple resistances connected in
series and parallel.
Components
|
Name
|
EDWin Components Used |
Description |
Number of components
required |
| RES |
RC05 |
Resistor |
2 |
| VDC |
VDC |
Dc voltage source |
1 |
| GND |
SPL0 |
Ground |
1 |
Theory
- Series Resistances
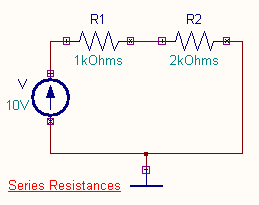
When resistors are connected in series
 Same current flows through each resistor
Same current flows through each resistor
 The voltage drop across each resistor will be different.
The voltage drop across each resistor will be different.
 The applied voltage is equal to the sum of the voltage drops across individual resistor.
The applied voltage is equal to the sum of the voltage drops across individual resistor.
 Voltage drops are additive, resistances are additive
Voltage drops are additive, resistances are additive
 Powers are additive
Powers are additive
Total voltage applied,
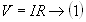
Where I is the current through the circuit and R is the total resistance
of the circuit.
Voltage drop across 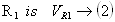
Voltage drop across 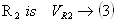
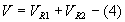
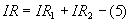
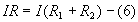
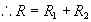 which is the
equivalent series resistance.
which is the
equivalent series resistance.
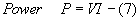
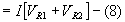
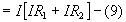
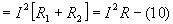
- Parallel Resistances
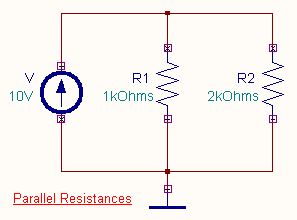
When resistances are connected in parallel
 Same voltage acts across all resistors of the circuit
Same voltage acts across all resistors of the circuit
 Current flowing through each resistor varies.
Current flowing through each resistor varies.
 Branch currents are additive
Branch currents are additive
 Conductances are additive
Conductances are additive
 Powers are additive.
Powers are additive.
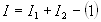
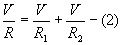
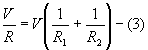
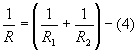
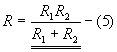
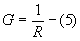
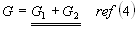
Power,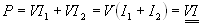
Procedure
EDWinXP-> Schematic Editor:
The circuit diagram is drawn by loading components
from the library. Wiring and proper net assignment has been made. The values are
assigned for relevant components. The series and parallel resistance
circuit diagrams in the Mixed mode simulator is shown below.
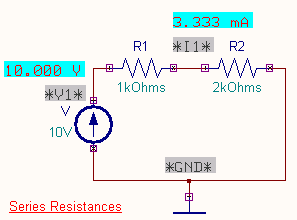
EDWinXP -> Mixed Mode Simulator: The circuit is preprocessed. The
desired test points and waveform markers are placed. The Transient
Analysis parameters have been set. The Transient Analysis is executed. The
test points display the values of the current through the resistors as shown.
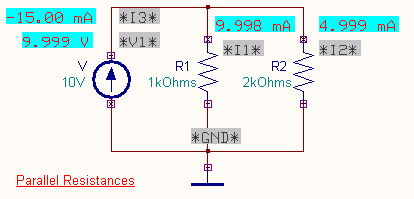
The variation of current through the two resistors with respect to
variation in voltage is obtained by performing DC Sweep Analysis on
both series and parallel resistance circuits. To perform DC Sweep Analysis a
current waveform marker is placed. The sweep parameter (voltage) for input source is set in the Analysis window. The applied voltage
is swept from an initial value of 0 to final value of 10V in steps of
100mV. The DC Sweep Analysis is executed and the
corresponding waveforms are observed in the Waveform Viewer.
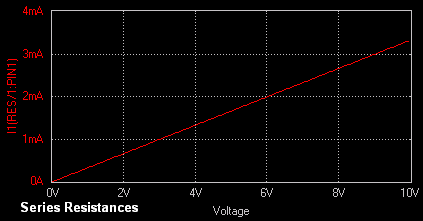
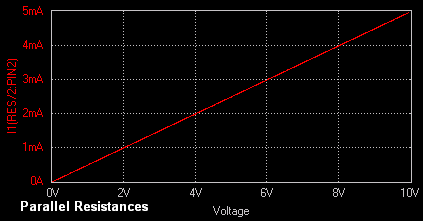
Result
The output waveform may be
observed in the waveform viewer. The output waveforms of DC Sweep Analysis for series and parallel
resistance
circuits are shown below. From the graphs it is
evident that the effective of the two similar resistances when connected
in series will be greater
compared to the case when they are connected in
parallel.